Introduction to Natural Emulsifiers
In the realm of product formulation, one of the most persistent challenges is the immiscibility of oil and water, which can lead to separation, reduced shelf life, and poor texture in various consumer goods. Emulsifiers are the key to overcoming this hurdle, and among the most effective and environmentally friendly options are Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates. Derived from renewable plant-based sources, these non-ionic surfactants have revolutionized industries by enabling stable emulsions in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and beyond. At FoodEmul.com, we specialize in providing high-quality Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates that cater to diverse needs, ensuring products are not only functional but also safe and sustainable. This guide delves deep into their origins, properties, and applications, offering insights into why they are indispensable in modern manufacturing.
What Are Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates?
Natural and Renewable Origins
Sorbitan Esters are synthesized through the esterification of sorbitol, a sugar alcohol derived from crops like corn and potatoes, with various fatty acids such as lauric, palmitic, stearic, or oleic acid. This process, often involving dehydration at high temperatures, results in the formation of sorbitan, which is then esterified to produce lipophilic surfactants. These compounds are entirely based on renewable raw materials, making them an eco-conscious choice for manufacturers aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. Similarly, Polysorbates are created by ethoxylating Sorbitan Esters, where ethylene oxide is added to enhance their hydrophilicity. This modification transforms them into versatile emulsifiers capable of handling oil-in-water systems, while maintaining their plant-based origins. The use of such natural sources aligns with global trends towards sustainability and green chemistry, positioning Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates as forward-thinking ingredients in various sectors.
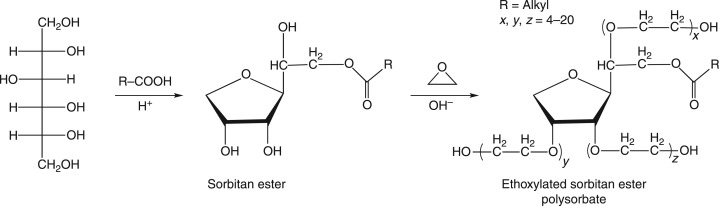
The Sorbitan Ester Family: Meet the Spans
The Sorbitan Ester family, commonly referred to as Spans, includes a range of esters each tailored for specific applications. For instance, Sorbitan Monolaurate (Span 20) is derived from lauric acid and is typically a liquid, ideal for emulsifying oil and water in cosmetic formulations. Sorbitan Monostearate (Span 60), made from stearic acid, appears as waxy flakes and is widely used in food products like margarine for its stabilizing properties. Other members include Sorbitan Monopalmitate (Span 40), Sorbitan Trioleate (Span 85), and Sorbitan Tristearate (Span 65), each with unique physical forms—from liquids to solids—and chemical characteristics. The numbering system (e.g., 20, 40, 60, 80) directly correlates with the fatty acid used: 20 for monolaurate, 40 for monopalmitate, 60 for monostearate, and 80 for monooleate. This variety allows formulators to select the most appropriate ester based on factors like HLB value, solubility, and desired emulsion type, ensuring optimal performance in end products.
| Nom du produit | Abbreviation | Physical Form | Primary Function | Principales applications | Industries Served | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbitan Mono Laurate | SML | Liquid | Emulsifier | Creams, lotions, sunscreens, topical formulations | Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals | Mild surfactant; suitable for sensitive skin; improves texture and skin feel; enhances emulsion stability |
| Sorbitan Mono Stearate | SMS | Waxy flakes | Food-grade emulsifier (W/O) | Margarine, ice cream, bakery products | Food, Cosmetics | Stabilizes water-in-oil emulsions; improves texture and consistency; prevents separation |
| Sorbitan Tri Stearate | STS | Waxy flakes | Lubricant | Fiber processing, coatings, industrial formulations | Textiles, Industrial, Coatings | Reduces friction; prevents static build-up; enhances fiber smoothness; improves process efficiency |
| Sorbitan Mono Oleate | SMO | Liquid | Stabilizer & lubricity additive | Lotions, creams, shampoos, dispersions | Cosmetics, Personal Care | Enhances smoothness and texture; improves emulsification; disperses active ingredients effectively |
| Sorbitan Tri Oleate | STO | Liquid | Emulsifier for balanced pH systems | Creams, lotions, pharmaceutical formulations | Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, Industrial | Excellent emulsifying ability; stable over wide pH range; mild to skin; enhances texture and stability |
Polysorbates: The Ethoxylated Partners
Polysorbates are ethoxylated derivatives of Sorbitan Esters, created by reacting them with ethylene oxide to introduce polyoxyethylene chains. This process significantly increases their hydrophilicity, resulting in HLB values ranging from 10.0 to 16.7, which makes them excellent for oil-in-water emulsions and solubilization. Common types include Polysorbate 20 (from monolaurate), Polysorbate 40 (from monopalmitate), Polysorbate 60 (from monostearate), and Polysorbate 80 (from monooleate). These surfactants are often used in tandem with Sorbitan Esters to achieve a balanced HLB, enabling the creation of emulsions with varying textures and consistencies. For example, in cosmetic creams, a blend of Sorbitan Stearate and Polysorbate 60 can produce a stable, smooth formulation. Their ability to enhance wetting, dispersing, and stabilizing properties makes Polysorbates invaluable in pharmaceuticals, where they are used in vaccines and injectables to ensure homogeneity and efficacy.

The Science of Emulsification: Understanding HLB
What is the HLB Value?
The Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) is a fundamental concept in surfactant science, quantifying the balance between the water-attracting (hydrophilic) and oil-attracting (lipophilic) portions of a molecule. Ranging from 1 to 20, the HLB value dictates the surfactant’s behavior in emulsions: values below 6 indicate a preference for water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions, while values above 8 favor oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions. Intermediate values around 7-9 are often associated with wetting agents. For Sorbitan Esters, HLB values are typically low, between 1.6 and 8.6, due to their lipophilic nature, making them ideal for W/O systems. In contrast, Polysorbates have high HLB values of 10.0 to 16.7, driven by their ethoxylated groups, which enhance water solubility and O/W emulsion formation. Understanding HLB is crucial for formulators, as it guides the selection of emulsifiers to achieve desired product characteristics, such as viscosity, stability, and texture.
Combining HLB for Perfect Formulations
One of the key advantages of Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates is their compatibility, allowing for precise HLB tuning through blending. By mixing a low-HLB Sorbitan Ester with a high-HLB Polysorbate, manufacturers can target a specific HLB value suited to their application. For instance, combining Sorbitan Monostearate (HLB 4.7) with Polysorbate 60 (HLB 14.9) can yield an HLB around 9.8, ideal for O/W emulsions in lotions or food products. This synergy enables the creation of emulsions with tailored properties, from thick, creamy W/O formulations in cosmetics to light, fluid O/W systems in beverages. Practical examples include ice cream, where such blends prevent ice crystal formation and improve mouthfeel, or in pharmaceutical creams, where they ensure even drug distribution. The ability to customize HLB not only enhances product performance but also reduces the need for multiple ingredients, streamlining formulations and cutting costs.
Key Applications Across Industries
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food sector, Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates serve as essential food-grade emulsifiers, approved by regulatory bodies like the WHO for their safety. Sorbitan Monostearate, for example, is widely used in margarine and spreads to stabilize W/O emulsions, preventing oil separation and ensuring a smooth consistency. In ice cream, it helps control overrun and texture by promoting air incorporation and reducing ice crystal size. Polysorbates, such as Polysorbate 80, are employed in sauces, dressings, and baked goods to maintain homogeneity and enhance shelf life. Their role extends to confectionery, where they prevent sugar crystallization, and in beverages, they aid in flavor solubilization. The plant-based origin of these emulsifiers appeals to health-conscious consumers, while their non-toxic nature ensures compliance with food safety standards, making them a staple in modern food processing.
Cosmetic and Personal Care
The cosmetic industry relies heavily on Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates for their emulsifying, stabilizing, and texturizing properties. Sorbitan Esters like Sorbitan Monooleate are used in creams and lotions to create stable W/O emulsions that provide a rich, non-greasy feel on the skin. In sunscreens, they help disperse UV filters evenly, enhancing protection. Polysorbates, with their high HLB, are ideal for O/W formulations in products like shampoos and conditioners, where they solubilize fragrances and active ingredients while improving foam and rinseability. Their mildness makes them suitable for sensitive skin formulations, reducing irritation risks. Additionally, these surfactants contribute to product aesthetics by ensuring smooth application and long-lasting stability, which is critical in competitive markets where consumer satisfaction drives brand loyalty.
Pharmaceutical Applications
In pharmaceuticals, Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates play a critical role in formulating stable emulsions, creams, and ointments. They are used to evenly disperse active pharmaceutical ingredients, ensuring consistent dosage and efficacy. For instance, in topical treatments, Sorbitan Monolaurate can enhance skin penetration of drugs, while Polysorbate 80 is common in injectables and vaccines, where it stabilizes proteins and prevents aggregation. Their safety profile, backed by extensive toxicological studies, makes them suitable for sensitive applications, including pediatric and geriatric products. Regulatory approvals from agencies like the FDA and EMA underscore their reliability, with established ADI values ensuring safe consumption. The ability to tailor HLB through blends allows for customized formulations that meet specific therapeutic needs, from anti-inflammatory creams to life-saving vaccines.
Industrial and Technical Uses
Beyond consumer goods, Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates find applications in various industrial sectors. Sorbitan Tristearate, for example, is used as a lubricant in textile manufacturing, reducing friction between fibers during spinning and weaving, which minimizes wear and improves product quality. In plastics, they serve as anti-fogging agents in films, preventing condensation that could obscure visibility. The agrochemical industry employs them as dispersants in pesticides and herbicides, ensuring even coverage and enhanced efficacy. Additionally, they are used in metalworking fluids as corrosion inhibitors and in polymerization processes as emulsifiers. Their versatility stems from their non-ionic nature, which makes them less sensitive to pH and electrolyte changes, allowing for consistent performance in harsh industrial environments. This broad applicability highlights their value as multi-functional additives that boost efficiency and sustainability across technical fields.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by international bodies such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Extensive studies have shown them to be non-toxic, non-irritating, and non-sensitizing, with acute and chronic exposure data confirming their safety for human use. The ADI (Acceptable Daily Intake) for common Sorbitan Esters is set at 0-25 mg/kg body weight per day, reflecting their low risk profile. During digestion, they are hydrolyzed into sorbitan and fatty acids, which are metabolized or excreted harmlessly. Their plant-based origin further enhances their appeal, catering to vegan and natural product trends. In cosmetics, they are listed in positive regulatory databases, and in pharmaceuticals, they meet stringent purity standards. This robust safety framework ensures that manufacturers can use these emulsifiers with confidence, knowing they align with global health and environmental guidelines.
Choosing the Right Emulsifier from FoodEmul.com
Selecting the appropriate Sorbitan Ester or Polysorbate depends on factors like HLB value, application, and desired emulsion type. At FoodEmul.com, we offer a comprehensive range of these emulsifiers, including Sorbitan Monolaurate, Monostearate, Trioleate, and various Polysorbates, all sourced from renewable plants. Our products are customizable to meet specific client needs, whether for food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, or industrial uses. With expertise in HLB systems, we assist formulators in blending emulsifiers to achieve optimal results, such as stable emulsions, improved texture, and enhanced shelf life. By partnering with us, you gain access to high-quality, safe ingredients that support innovation and sustainability in your products. Explore our offerings to find the perfect emulsifier solution for your next formulation challenge.

